- ACLS BLS for Adults
- Initiating the Chain of Survival
- 2020 BLS Guideline Changes
- One Rescuer Adult BLS CPR
- Two Rescuer Adult BLS CPR
- Adult Mouth-to-Mask and Bag-Mask Ventilation
- Adult Basic Life Support (BLS) Algorithm
- BLS for Children/Infants
- CPR Steps for Children
- One-Rescuer BLS/CPR for Infant (newborn to age 12 months)
- CPR Steps for Infants
- Child/Infant Mouth-to-Mouth Ventilation
- ACLS Cases Respiratory Arrest
- Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia and Ventricular Fibrillation
- Pulseless Electrical Activity Asystole
- Adult Cardiac Arrest Algorithm
- Post-Cardiac Arrest Care
- Adult Immediate Post-Cardiac Arrest Care Algorithm
- Symptomatic Bradycardia
- Adult Bradycardia with Pulse Algorithm
- Tachycardia
- Stable And Unstable Tachycardia
- Adult Tachycardia With Pulse Algorithm
- Acute Coronary Syndrome
- Acute Coronary Syndrome Algorithm
- Acute Stroke
- Acute Stroke Algorithm
Adult Bradycardia with Pulse Algorithm
Understanding and effectively applying the ACLS bradycardia algorithm is essential for health care professionals managing patients with symptomatic bradycardia with a pulse. Prompt recognition and intervention can prevent the progression to more severe cardiac events. This guide provides an overview of the key aspects of the ACLS bradycardia algorithm, incorporating critical dosing details to enhance your ability to respond effectively during emergencies.
Importance of the ACLS Bradycardia Algorithm
The ACLS bradycardia algorithm is a systematic approach designed to assist clinicians in:
- Accurate Assessment: Determining the severity of the patient’s bradycardia with pulse and its impact on hemodynamic stability.
- Identifying Underlying Causes: Recognizing reversible factors contributing to the bradycardia.
- Appropriate Intervention: Implementing treatments based on the patient’s condition, including specific medication dosages and pacing when necessary.
By adhering to the ACLS bradycardia algorithm, health care providers can improve patient outcomes and reduce the risk of deterioration to cardiac arrest.
Adult Bradycardia with Pulse Algorithm
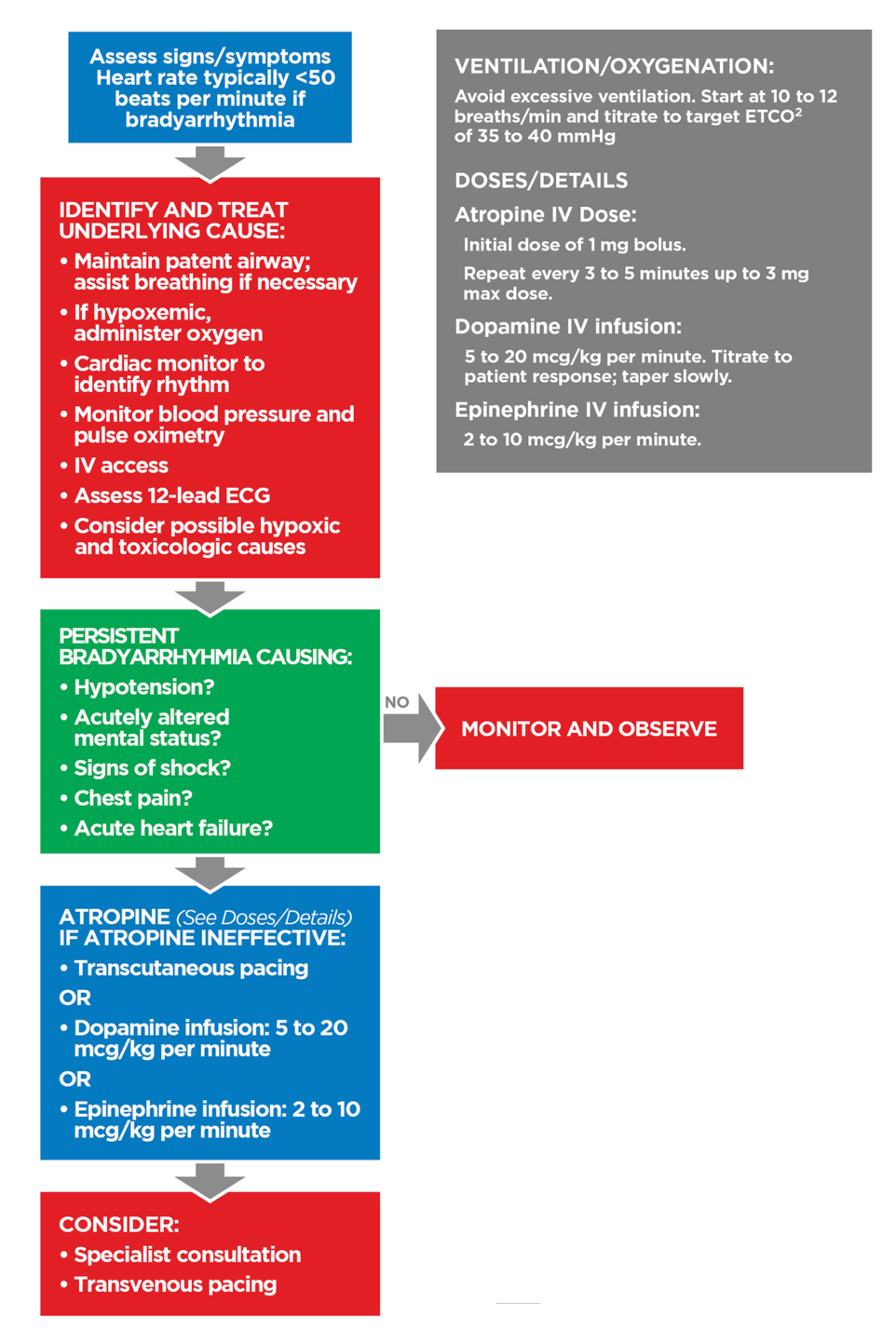
Key Steps of the ACLS Bradycardia Algorithm
1. Assess and Monitor the Patient
- Airway and Breathing: Ensure the airway is open and the patient is breathing adequately; provide oxygen if needed.
- Circulation: Monitor blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation.
- Vital Signs: Obtain a complete set of vital signs, including level of consciousness.
- Establish IV Access: Prepare for medication administration.
- 12-Lead ECG: obtain an ECG and identify the type of bradycardia.
2. Evaluate for Signs of Poor Perfusion
- Symptoms of Unstable Bradycardia with Pulse:
- Hypotension
- Altered mental status
- Signs of shock
- Chest pain
- Acute heart failure
3. Identify and Treat Underlying Causes
Consider possible contributing factors to bradycardia (remember the H’s and T’s):
- Hypoxia
- Hypothermia
- Hypovolemia
- Hyper/Hypokalemia
- Toxins
- Tamponade (cardiac)
- Tension pneumothorax
- Thrombosis (coronary or pulmonary)
4. Implement Appropriate Interventions
If the Patient is Symptomatic (Unstable Bradycardia with Pulse)
First-line Medication: Atropine
- Atropine IV Dose:
- First Dose: 0.5 mg bolus
- Repeat: Every 3-5 minutes as needed
- Maximum Total Dose: 3 mg
If Atropine is Ineffective
Proceed to one of the following:
- Transcutaneous Pacing
- Dopamine Infusion
- Dopamine IV Infusion Dose:
- 2-20 mcg/kg per minute
- Titrate to patient response
- Taper slowly as needed
Epinephrine Infusion
- Epinephrine IV Infusion Dose:
- 2-10 mcg per minute
- Titrate to patient response
5. Consider Expert Consultation
If the patient does not respond to initial treatments or if the management plan is uncertain, seek expert consultation.
6. Prepare for Transvenous Pacing
If the patient remains unstable despite medications and transcutaneous pacing, prepare for transvenous pacing.
Doses and Details
Atropine IV Dose
- Initial Dose: 0.5 mg IV bolus
- Repeat: Every 3-5 minutes as needed
- Maximum Total Dose: 3 mg
Dopamine IV Infusion
- Dose Range: 2-20 mcg/kg per minute
- Administration: Titrate to patient response; taper slowly
Epinephrine IV Infusion
- Dose Range: 2-10 mcg per minute
- Administration: Titrate to patient response
Transcutaneous Pacing
- Procedure: Apply pacing pads and begin pacing at the lowest effective energy level.
- Monitoring: Observe patient comfort and adjust settings as necessary
Enhance Your Skills with Our Online ACLS Certification Course
Continuous education and practice are essential to apply the ACLS bradycardia algorithm effectively. Enroll in our Online ACLS Certification Course to:
- Deepen Your Knowledge: Comprehensive modules covering all Advanced Cardiac Life Support aspects, including bradycardia management.
- Improve Competency: Interactive scenarios to practice critical decision-making.
- Earn Accreditation: Receive a certification recognized by health care institutions nationwide.
- Flexible Learning: Study at your own pace with 24/7 access to course materials.
- Immediate Certification: Obtain your digital certificate upon successful completion.
Commitment to Excellence in Cardiac Care
Mastering the ACLS bradycardia algorithm empowers health care professionals to deliver lifesaving interventions confidently. By staying current with the latest guidelines and refining your skills—including understanding dosing specifics—you contribute to better patient outcomes and demonstrate your dedication to high-quality emergency care.
